How to Add a New Resource
How to Add a Resource to GMAT
Wendy Shoan, GSFC, Code 583
February 3, 2015
Introduction
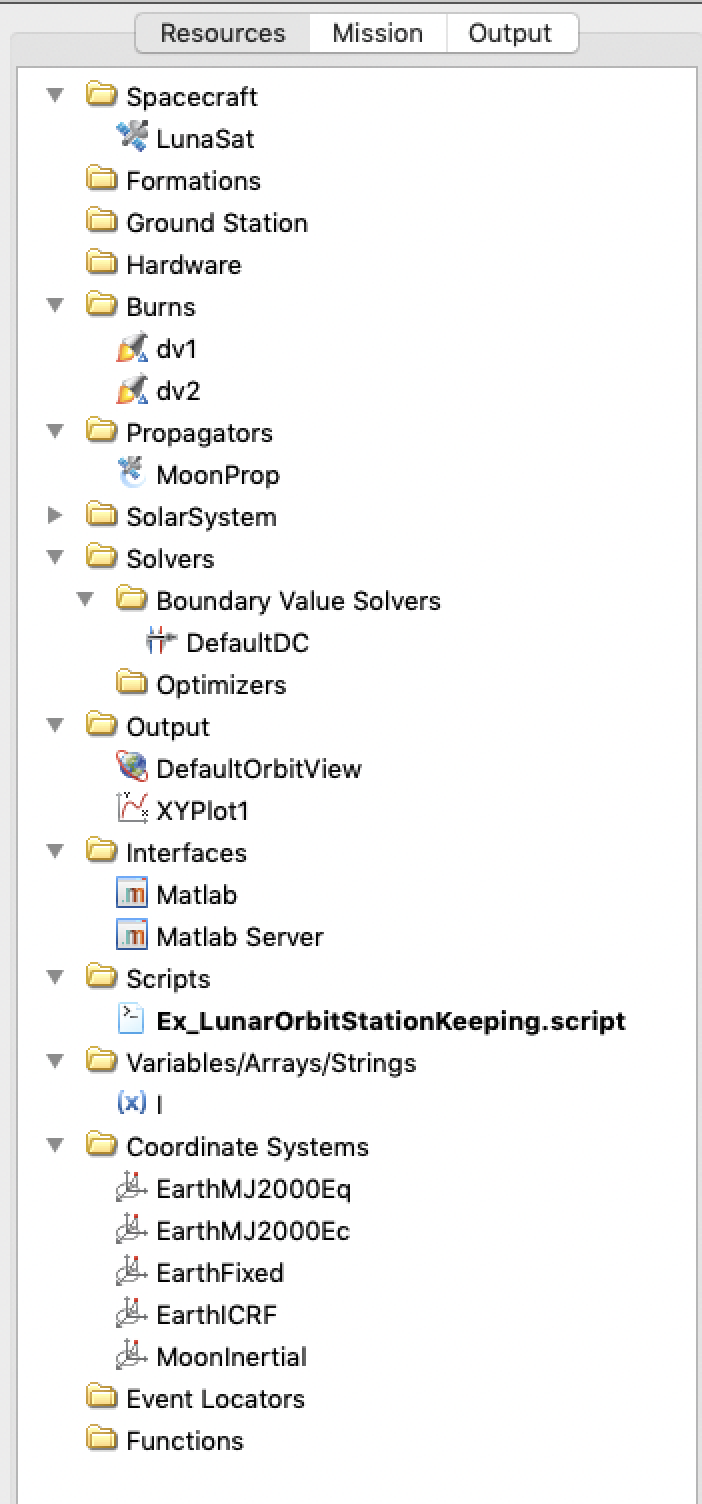
GMAT has the capability to model many types of Resources, for use in various types of space missions. Resources in GMAT are created, via script or GUI, and used by other Resources or in Commands, to run a particular mission of interest. Here is an example of the scripting of Resources for, in this case, a Lunar Orbit StationKeeping script:
Create Spacecraft LunaSat;
GMAT LunaSat.DateFormat = TAIModJulian;
GMAT LunaSat.Epoch = '21545';
GMAT LunaSat.CoordinateSystem = MoonInertial;
%% [...] other statements to configure the LunaSat resource
Create ForceModel MoonProp_ForceModel;
GMAT MoonProp_ForceModel.CentralBody = Luna;
GMAT MoonProp_ForceModel.PrimaryBodies = {Luna};
GMAT MoonProp_ForceModel.PointMasses = {Earth, Jupiter, Sun};
%% [...] other statements to configure the ForceModel resource
Create Propagator MoonProp;
GMAT MoonProp.FM = MoonProp_ForceModel;
GMAT MoonProp.Type = PrinceDormand78;
%% [...] other statements to configure the MoonProp resource
Create ImpulsiveBurn dv1;
GMAT dv1.CoordinateSystem = Local;
GMAT dv1.Origin = Luna;
GMAT dv1.Axes = VNB;
%% [...] other statements to configure the dv1 resource
Create ImpulsiveBurn dv2;
GMAT dv2.CoordinateSystem = Local;
GMAT dv2.Origin = Luna;
GMAT dv2.Axes = VNB;
%% [...] other statements to configure the dv2 resource
Create Variable I;
Create CoordinateSystem MoonInertial;
GMAT MoonInertial.Origin = Luna;
GMAT MoonInertial.Axes = BodyInertial;
%% [...] other statements to configure the MoonInertial resource
Create DifferentialCorrector DefaultDC;
GMAT DefaultDC.ShowProgress = true;
%% [...] other statements to configure the DefaultDC resource
Create OrbitView DefaultOrbitView;
GMAT DefaultOrbitView.Add = {LunaSat, Luna};
GMAT DefaultOrbitView.CoordinateSystem = MoonInertial;
%% [...] other statements to configure the OrbitView
Create XYPlot XYPlot1;
GMAT XYPlot1.XVariable = LunaSat.A1ModJulian;
GMAT XYPlot1.YVariables = {LunaSat.Luna.RadPer};
%% [...] other statements to configure the XYPlot
The corresponding Resource Tree, showing the Resources defined in the script, looks like this:
GMAT provides many types of Resources that are useful in modeling Spacecraft Missions. However, you may need a particular type of resource that is not included in GMAT. In this case, you can add the needed resource to GMAT. There are two types of additions to discuss:
Case 1: In the simpler case, a new subtype of an existing resource type may be required. For example, a mission might require a new type of Thruster, and in this case, you can add to GMAT the code necessary to allow objects of the new Thruster type to be created and used in a mission.
Case 2: In a more complex case, an entirely new class of Resource needs to be created. You can add the new class of Resource to GMAT, along with other supporting code.
In both cases, you will also have to modify other executive and GUI classes to handle the new resource type or subtype.
This document describes a general procedure to follow in order to add a new Resource type or subtype to the baseline GMAT code. There are also considerations specific to the type of resource to be added, e.g., for a new type of Thruster, the Spacecraft and FiniteBurn code may need to be modified to allow use of the new type. This document will not specifically address these resource-specific issues.
If you would prefer to add your new functionality as a plugin, please also see the document "Building a GMAT Plug-in: A Walkthrough Using Visual Studio 2010".
Overview
GMAT has a base class, GmatBase, from which all configurable resource types must be derived. There are often intermediate classes as well, to encapsulate common data and methods for the resource type. For example, there is a CelestialBody class, which derives from the SpacePoint class (which itself derives from GmatBase) and from which Star, Planet, Moon, Comet, and Asteroid are derived [See Figure]. Data and method implementations that are common to all five of these subclasses are placed in the CelestialBody class, and only those that need specific modifications are added or overridden in the leaf classes. Similarly, methods and data common to all SpacePoint objects are encapsulated in the SpacePoint class, and are thus inherited by derived classes. At the top of the inheritance path, GmatBase provides many methods, data definitions, and settings that are useful to derived Resource classes.
Since a user must set relevant and/or required data on each Resource in order to specify the desired behavior of the resource, the process of adding a new resource to GMAT will include the requirement to, if applicable, provide appropriate user-settable data, or properties (with reasonable defaults), and related methods for the resource so that it can be used as part of the mission. For example, the Spacecraft class defines a CoordinateSystem property that a user may set and which is used by its methods. In addition, GMAT classes performing script interpretation, mission execution, object mapping, and other executive functions, require other methods that must be implemented in Gmatbase-derived classes.
Methods for Initialization, Copy, and Cloning
These are a few examples of methods that may require implementation:
bool Initialize():
This method is called at the beginning of the run, to initialize internal data needed by the resource, and to perform validation of user input values.
void Copy(const GmatBase*):
This method is called to copy the input object's data to the current one.
GmatBase* Clone() const:
This method is called to return a clone of the object. [required on all leaf classes]
Methods for Script User Interfaces
As mentioned, there are properties of your resource that a user may inspect or optionally set. When you define a property for your resource, you need to answer some questions:
- Is the property read-only or can it be set by the user of your resource?
- What is the type of the property?
Each of your new properties must be added to the enumeration in the header which lists available properties, and to the string array specifying the string representation of the property. This will be used by GMAT scripting for access to the properties. GmatBase provides methods for accessing these properties. Based on how you answered the questions above, you will need to override the following methods:
std::string GetParameterText(const Integer id) const:
This method returns the text representation of a specified parameter, given the id.
std::string GetParameterUnit(const Integer id) const:
This method returns the units of a specified parameter, given the id. [useful for the GUI for your class]
Integer GetParameterID(const std::string &str) const:
This method returns the id of a specified parameter, given the text.
Gmat::ParameterType GetParameterType(const Integer id) const:
This method returns the Gmat type of the specified parameter. The enumeration ObjectType in gmatdefs.hpp defines the parameter types.
std::string GetParameterTypeString(const Integer id) const:
This method returns string representation of the Gmat type of the specified parameter.
bool IsParameterReadOnly(const Integer id) const:
This method returns true if the specified parameter is read-only – that is, the user will not be allowed to modify it. This may be necessary if you want parameters available for other parts of the system to set but not available to the user.
Real GetRealParameter(const Integer id) const:
This method returns the Real value of the specified parameter.
Real SetRealParameter(const Integer id, const Real value) :
This method sets the Real value of the specified parameter.
NOTE: there are equivalent Get/Setmethods for other types – Integer, UnsignedInt, UnsignedIntArray, IntegerArray, Rvector, Rmatrix, String, StringArray, OnOff, Boolean, BooleanArray – that may need to be implemented, depending on the types of data needed for your class.
Methods for Setting Reference Objects
If your class needs reference objects set (for example, your class needs to access a Spacecraft object), you will need to implement additional methods, for example:
std::string GetRefObjectName(const Gmat::ObjectType type) const:
This method returns the name of the reference object of the specified type. [The name of the reference object is usually set by the user – this will be set via the SetStringParameter method or the SetRefObjectName method (see below)]
const StringArray& GetRefObjectNameArray(const Gmat::ObjectType type):
This method returns an array of the names of the reference objects of the specified type.
bool SetRefObjectName(const Gmat::ObjectType type, const std::string &name):
This method sets the name of the reference object of the specified type.
bool SetRefObjectName(const Gmat::ObjectType type, const std::string &name):
This method sets the name of the reference object of the specified type.
bool SetRefObject(GmatBase *obj, const Gmat::ObjectType type, const std::string &name):
This method sets the pointer to the reference object with the specified name and type.
This is just an example of the methods that may need to be implemented for your new class. Please see GmatBase.hpp for the complete list of base methods. It is extremely helpful to find a class similar in function to your new class to determine what other methods/data may need to be included or overridden.
Required Code for Type Determination
In GmatBase, we have two arrays – objectTypes and objectTypeNames – that specify the type of object. In each class, the constructor must add to these in order for the system to know the correct type for each object. These are arrays, so each subclass will add its type. For example, a Barycenter is derived from CalculatedPoint, which itself is derived from SpacePoint. So, by setting these types in each class, a Barycenter knows that it is a Barycenter, a CalculatedPoint, and a SpacePoint object. This is set in the default constructor for Barycenter:
objectTypes.push_back(Gmat::BARYCENTER);
objectTypeNames.push_back("Barycenter");
and for CalculatedPoint:
objectTypes.push_back(Gmat::CALCULATED_POINT);
objectTypeNames.push_back("CalculatedPoint");
and for SpacePoint:
objectTypes.push_back(Gmat::SPACE_POINT);
objectTypeNames.push_back("SpacePoint");
In addition, each class must set its parameterCount based on its own enumeration:
parameterCount = BarycenterParamCount;
Required First Steps
In order to add a new Resource to GMAT, some preliminary steps must be taken to set up your build environment:
1. Download the configured GMAT source
2. Download, or refer to, the GMAT C++ Code Style Guide from the GMAT Wiki – standard GMAT coding style must be followed for any new/modified code.
3. Build GMAT on your platform with no code changes (see instructions on building on GMAT Wiki) [NOTE: to maintain cross-platform compatibility, code must build successfully using the gcc compiler in order to be considered for inclusion into GMAT]
4. Run Sample Missions (or SmokeTests* and possibly a subset of relevant system test folders, if you have access to those) before code modification, to
1) Confirm successful execution of the unmodified GMAT, and
2) Obtain an initial set of 'truth' data for later testing
Once these steps have been completed and GMAT runs successfully as-is, addition of the new resource may begin.
General Requirements
Though GMAT is a modular system, adding a new resource is not as simple as just compiling and linking a new class. There are requirements that must be met regarding, among other things:
- Deriving from base classes (either an existing resource class, or
GmatBase) - Implementing, at a minimum, specific methods
- Adding a new type to the appropriate factory (or creating a new factory) that knows how to create your new resource
- Updating base type lists and related enumerated types
- Adding and/or modifying types and methods in GUI management classes
- Determining look-and-feel of GUI components added for the new resource
The steps required to create and add a new resource to GMAT are described below.
Recommended Practices
There are practices and/or strategies that may be helpful to a developer in creating a new component, e.g., sometimes it is helpful to:
- First, determine scripting of the new component
- Next, modify/add the minimal set of code for the new resource until the script parses
- Then, add validation of the input data
- Next, incrementally add and validate new functionality until the resource is complete
Adding a New Resource Subtype of an Existing Type (Type 1)
Initial Steps
- Decide on the scripting needed to create and access your new resource, as best as you can.
- Determine the public properties needed, their valid values, and how the class will be used in GMAT.
Base Code modifications
- Decide which GMAT resource base class will be the parent of your new class. For example, if you are adding a new type of Thruster, you will need to derive your class from the base
Thrusterclass, located in src/base/hardware. - Determine whether or not you can copy-and-paste portions of your new class from an existing class. If not, you will need to start from scratch, deriving your class from the base class you selected in the previous step. In either case, make sure the standard header information is present and correct, and your new code follows the GMAT C++ Style Guide.
- Add additional data or methods to the new class as needed. If you add additional user-settable parameters, you will need to create an enumeration listing those new data, as well as static string and
Gmat::ParameterTypearrays to hold the strings and data types for those new parameters (see Appendix A example). - Implement the pure virtual methods of the parent class (or inherited by the base class), and other public methods whose base/default implementation are not correct or sufficient for your new class. For example, if you need to add some validation to the Initialize() method, you would include new code in your
Initialize()method and (almost certainly) call the parentInitialize()from your method as well. - If your class is a leaf class, implement the
Clone(and potentially,Copy) methods. - If you do not have any reference objects, use "
DEFAULT_TO_NO_REFOBJECTS" in the public part of your header file. - If you do not have any owned clone members, use "
DEFAULT_TO_NO_CLONES" in the public part of your header file. - Add your new type to the appropriate
Factorysubclass in /src/base/factory. - Add your new resource name to the
ObjectTypeenum in include/gmatdefs.hpp. - Add to
OBJECT_TYPE_STRINGandAUTOMATIC_GLOBAL_FLAGSin GmatBase.cpp, being careful to add your new entries in the correct spot in each. - Implement validation of your added class data, following the style of other classes (e.g. using
errorMessageFormat, etc.) - Implement the functionality of the new class.
- Add your new class(es) to the MakeBase.eclipse file to make sure it is compiled.
- Add your new resource class to the Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 Express libGmatBase project if you are building using MS Visual Studio.
GUI Code modifications
- Add your new type to
GuiTreeItemData::ItemTypeif appropriate. - Check the
CreateNewResource()method in theGmatMainFrameclass to see if you need to add or modify the list (e.g. in the switch statement), to match the modifications toGmatTreeItemData. - Decide whether you can use the
GmatBaseSetupPanel, or if you will need a custom GUI panel for your new resource. See How to Create GMAT Panels for further instructions on creating a new GUI panel. NOTE that if you use theGmatBaseSetupPanel, you will also need to implement these methods in your new base class: GetPropertyObjectType and GetTypesForList (if you have a parameter ofOBJECT_ARRAYtype) - In the
ResourceTreeclass, you may need to modify or add methods for your new type, e.g. the OnAdd* methods. Also, add item(s) to thePOPUPenum for your class, or modify existing items as needed. - You will need to add (or modify) methods in
GuiItemManagerthat keep a list of configured objects of your new type and update that list when necessary, and create/unregister GUI widgets (e.g. combo boxes or lists) that may be needed - Add your new class(es) to the MakeGui.eclipse file to make sure it is compiled
- Add your new resource class to the Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 Express GMAT_wxGui project if you are building using MS Visual Studio.
Adding a New Resource Type (Type 2)
For this case, there are several steps that must be taken before completing the steps listed above.
Base Code
Since you are creating a new Resource 'from scratch', you will need to tell GMAT about the new Resource. There are several places in GMAT where you will need to update the code.
- You need to make an entry in the gmatdefs.hpp
Gmat::ObjectTypefor your new Resource. For example, if I were to add anErrorModelclass, I would add an ERROR_MODEL entry toObjectType. Your new entry should be in a location in the list that makes sense (for example, near similar items, or at the end immediately before the UNKNOWN_OBJECT entry). - There are two places in GmatBase.cpp that you will need to modify. You must make sure these additions are each inserted into the correct position in the array, corresponding to the position where you added your entry into
Gmat::OBJECT_TYPE.- First, you will need to add your class/Resource name to
OBJECT_TYPE_STRING. - Also, you will need to add to the
AUTOMATIC_GLOBAL_FLAGSarray.
- First, you will need to add your class/Resource name to
- Create your new class, making sure to derive it from
GmatBase. You will implement it as described above for Type 1, adding methods and data as needed, and implementing applicable methods inherited fromGmatBase. - You need to create a factory that will know how to create objects of your new Resource type. To do this, create the new
Factoryclass, e.g. ErrorModelFactory.hpp and ErrorModelFactory.cpp (see otherFactoryclasses for examples). You will want to make sure that it includes the CreateObject generic method – this is needed for compatibility with recentInterpreter/Moderatormodifications. - Because objects are generally configured, you need to tell the
ConfigManagerclass about your new Resource. You will need an Add method and a Get method for your new Resource, e.g. AddErrorModel and GetErrorModel. - The
Moderatoralso needs to know about your new Resource, so you will need to modify Moderator.cpp to register your new factory. - To ensure that the
Interpretercode can handle your new type: - Add a string array to Interpreter.hpp, e.g.
errorModelList - In
Interpreter::BuildCreatableObjectMaps, add a section for your new list. - In
Interpreter::GetCreatableList, add a section for you new type - To make sure that objects of your new class are written out correctly to a script, you will need to add to
ScriptInterpreter::WriteScript. Add code there, similar to that for other types, to write objects of your new type. - You may need to modify
ObjectInitializercode if you need objects of your type to be initialized before or after another specific type of object, or if you need to build references between your Resource type and objects of another type.
GUI Code
The steps for adding a panel and incorporating your new Resource into the other GUI code are identical to steps taken for Type 1.
System Test Readiness Criteria
Once you have completed your code modifications and additions, there are several criteria that must be met before the code will be accepted for inclusion into the GMAT base.
- Update your code base with the latest configured GMAT code, merging the configured code into your code base when necessary.
- Build with the gcc compiler
Then, for those with code modification and system test privileges:
- Run SmokeTests and the applicable resource and/or command system test folder(s) successfully
- Inform testers of changes to GUI components, when applicable
- Wait for approval/confirmation before checking your code in to the repository.
Or, for those without code modification and system test privileges:
- Run unit-tests with the new code – these unit-tests must be thorough and should use input test data obtained from GMAT engineers when available
- Coordinate with GMAT team members to deliver code modifications
Appendix A: Example (Type 1)
This appendix shows an example, illustrating the steps that need to be taken to add a NuclearPowerSystem class.
Initial Steps:
- Decide on the script syntax for the new resource, based on the data and functionality required. Decide on the fields needed. For example, based on the needed fields, we may need the scripting to include something like this:
GMAT NuclearPowerSystem1.AnnualDecayRate = 5.123; GMAT NuclearPowerSystem1.Margin = 4.998;
Base Code
Decide on the new class structure. Since we may need or want to add other Power Systems at a later time, we will derive a
PowerSystemclass fromHardwareand then derive aNuclearPowerSystemclass from that.Create the new resource class from scratch, or start from a similar class (derived from the same base type) and modify as needed. In this example, we can start from a similar
Hardwareclass and modify. Edit the header to make sure all the author, date, and descriptive information is correct:
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------ // PowerSystem //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ // GMAT: General Mission Analysis Tool. // // Copyright (c) 2002-2014 United States Government as represented by the // Administrator of The National Aeronautics and Space Administration. // All Other Rights Reserved. // // Author: Wendy C. Shoan // Created: 2014.04.28 // /** * Base class definition for the PowerSystem. */ //------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- For the
PowerSystembase class, it might be necessary to remove, or not implement,Hardwaredata and methods that are not needed. In this case, however, it looks like we will need all of the methods fromHardware. Add additional data or methods to the new class as needed. For example, since a basic requirement for a power system will be to compute and provide the available power, we will want to add these methods (among others) in the public part of the class:
virtual Real GetBasePower() const; virtual Real GetPowerGenerated() const = 0; // Total Power Available
and in the protected part of the class:
/// Annual Decay Rate
Real annualDecayRate;
/// Margin
Real margin;
/// Published parameters for all power systems
enum
{
EPOCH_FORMAT = HardwareParamCount,
INITIAL_EPOCH,
INITIAL_MAX_POWER,
ANNUAL_DECAY_RATE,
MARGIN,
// ... others here ... see Appendix for entire list
PowerSystemParamCount
};
/// Parameter labels
static const std::string
PARAMETER_TEXT[PowerSystemParamCount - HardwareParamCount];
/// Parameter types
static const Gmat::ParameterType
PARAMETER_TYPE[PowerSystemParamCount - HardwareParamCount];
The GetBasePower() method will be fully implemented here. However, other methods, including the GetPowerGenerated() method, may need to be fully implemented in a derived class. We could define a default implementation in the PowerSystem base class, or leave it as a pure virtual method (as we do here), to require an implementation in descendant classes.
- Implement the pure virtual methods of the parent class and other public methods whose base/default implementation are not correct or sufficient for your new class. Note that we don't need to implement the Clone method here, as it is only required in leaf classes. However, we will want to implement access methods (Get/Set) for Real and String parameters – they should perform as much input validation as it is possible to do at build time. In this case, we do not need to implement methods related to reference objects for this class.
- We will implement the Initialize method, though currently it is only a call-through to the parent
Hardwareclass. The Initialize method is used to do run-time validation of inputs (for things that cannot be verified at build time) and to check for unset reference objects. - Since the parent class,
Hardware, already contains "DEFAULT_TO_NO_CLONES" in its header, we do not need to add it here. - Since we don't know if a future derived class will require reference objects, we will not add "DEFAULT_TO_NO_REFOBJECTS" here. However, we will need to remember to add it to the leaf class,
NuclearPowerSystem, since that subclass has no reference objects. - Since this is not a leaf class, we do not need to add it to any factory class, such as the HardwareFactory.cpp. Again, this is a step we need to remember to perform for the leaf classes.
- We need to tell the system what type of resource this class is:
objectTypes.push_back(Gmat::POWER_SYSTEM);
objectTypeNames.push_back("PowerSystem");
In addition, remember that each class must set its
parameterCountbased on its own enumeration:parameterCount = PowerSystemParamCount;
- We also need to add this 'base'
PowerSystemclass to the main list of object types in gmatdefs.hpp, as other parts of GMAT may access objects by this general type:
POWER_SYSTEM, // for PowerSystems - We will add this new type to the OBJECT_TYPE_STRING in GmatBase.cpp, before the 'UnknownObject':
const std::string
GmatBase::OBJECT_TYPE_STRING[Gmat::UNKNOWN_OBJECT - Gmat::SPACECRAFT+1] =
{
"Spacecraft", "Formation", "SpaceObject", "GroundStation", "Burn",
// ... others here ... see Appendix
"DataFile", "ObType", "Interface", "MediaCorrection", "Sensor",
"RFHardware", "Antenna", "PowerSystem",
"UnknownObject"
};
- Since
PowerSystemobjects will not automatically be of global scope, we will also need to add 'false' to theAUTOMATIC_GLOBAL_FLAGSin GmatBase.cpp, being careful to add it at the correct spot in the array. - We should also add as much validation as possible to the Set<>Parameter methods. For example, in the SetRealParameter method, add this (among other modifications) to the switch statement:
case ANNUAL_DECAY_RATE:
if ((value >= 0.0) && (value <= 100.0))
annualDecayRate = value;
else
{
HardwareException hwe("");
hwe.SetDetails(errorMessageFormat.c_str(),
GmatStringUtil::ToString(value, 16).c_str(),
"AnnuaDecayRate", "0 <= Real Number <= 100");
throw hwe;
}
return annualDecayRate;
Be sure to always use the exception class relevant to the subsystem to which your new class belongs. Note the use of the errorMessageFormat string – this should be used whenever possible, to maintain consistency of error messages.
- Now we can start implementing the 'guts' of the
PowerSystemclass. This means implementing all remaining methods, including, for example, the GetBasePower method. - Our base
PowerSystemcode changes are complete for now. Add thePowerSystemclass to the list in MakeBase.eclipse file to make sure it is compiled. If you are developing on a Windows platform, you should also add the class to the project file for Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 Express.
GUI Code
GuiItemTreeData: We need to add our newPOWER_SYSTEMtype toGuiTreeItemData::ItemTypeenumeration.- In
GmatMainFrame, add the following code to the CreateNewResource method:
case GmatTree::POWER_SYSTEM: sizer->Add(new PowerSystemConfigPanel(scrolledWin, name), 0, wxGROW|wxALL, 0); break;
- For the power system class, we need a custom GUI panel. See How to Create GMAT Panels for further instructions on creating a new GUI panel.
- In the
GuiItemManagerclass, we need to do several modifications:- Remember to set
theNumPowerSystemin the constructors, and, as appropriate - Add the UpdatePowerSystem method referenced (see Appendix B)
- Add the methods GetPowerSystemComboBox and UpdatePowerSystemList (see Appendix B)
Modify the GetAttachedHardwareList method:
// Get requested spacecraft GmatBase *obj = theGuiInterpreter->GetConfiguredObject(scName.c_str()); if (obj) { StringArray tanks = obj->GetStringArrayParameter("Tanks"); StringArray thrusters = obj->GetStringArrayParameter("Thrusters"); std::string pwrSystem = obj->GetStringParameter("PowerSystem"); }Update the UpdateAll method with:
case Gmat::POWER_SYSTEM: UpdatePowerSystem(true); break;
and further down, with:UpdatePowerSystem(false); #if DBGLVL_GUI_ITEM_UPDATE MessageInterface::ShowMessage("======> after UpdatePowerSystem()\n"); #endif- In the UnregisterComboBox method, add:
else if (type == "PowerSystem") { std::vector<wxComboBox*>::iterator pos = find(mPowerSystemCBList.begin(), mPowerSystemCBList.end(), cb); if (pos != mPowerSystemCBList.end()) mPowerSystemCBList.erase(pos); }
- Remember to set
- In the
ResourceTreeclass, we need to add or modify code in several places:In the UpdateGuiItem method, add the following:
case GmatTree::POWER_SYSTEM: theGuiManager->UpdatePowerSystem(); break;
In the GetItemTypeAndIcon method, add the following:
else if (obj->IsOfType("PowerSystem")) { itemType = GmatTree::POWER_SYSTEM; itemIcon = GmatTree::RESOURCE_ICON_THRUSTER; // temporary - I need an icon for this! }- For this example, we are going to treat the
PowerSystemclass like other hardware plugins, even though it is not a plugin. This makes sense as there is already existing code to handle non-thruster, non-tank hardware objects. So, in OnAddHardware, we will need to check the type of the selection (see example code in Appendix B). We also need to add the
PowerSystemtype to the GetObjectType and GetTreeItemId methods' switch statements:case GmatTree::POWER_SYSTEM:
To make sure
PowerSystemitems are updated correctly, we need to add to the switch statement in the UpdateGUIItem method:case GmatTree::POWER_SYSTEM: theGuiManager->UpdatePowerSystem(); break;
- Now we should create our PowerSystemConfgPanel GUI Panel (please see How to Create GMAT Panels for more information).
- Since the
PowerSystemwill be 'attached' to aSpacecraft, we also need to create a panel to be used as a tab on theSpacecraftPanel. See thePowerSystemPanelheader in Appendix B. The implementation of this panel is very similar to that of existing 'tabs' used for theSpacecraftPanel. - Now, we need to add the
PowerSystemPanelandPowerSystemConfigPanelclasses to the list in MakeBase.eclipse file to make sure they are compiled. If you developing on a Windows platform, you should also add the classes to the project file for Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 Express.
Back to Base Code
- Now we need to create the subclass,
NuclearPowerSystem. We will derive it from thePowerSystemclass so that it inherits all of the methods and data we defined earlier. - In this case, recall that we have a pure virtual method, GetPowerGenerated, in the
PowerSystemclass. SinceNuclearPowerSystemis a leaf class, we must implement this method here. - Also, we must implement the Clone() method since this is a leaf class.
Each class must set its parameterCount based on its own enumeration:
parameterCount = NuclearPowerSystemParamCount;
- Add "DEFAULT_TO_NO_REFOBJECTS" to the leaf class.
- The class needs to tell the system what type of resource it is:
objectTypes.push_back(Gmat::NUCLEAR_POWER_SYSTEM); ** only needed if we add this type to GMAT::ObjectType
objectTypeNames.push_back("NuclearPowerSystem");
Back to GUI Code
No changes are needed here. We use the general PowerSystemConfigPanel class to configure our NuclearPowerSystem class.
Appendix B: Sample Code (Type 1)
Base Code
Code examples for the following are included here:
PowerSystem.hpp
NuclearPowerSystem.hpp
PowerSystem.cpp
NuclearPowerSystem.cpp
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// PowerSystem
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// GMAT: General Mission Analysis Tool.
//
// Copyright (c) 2002-2014 United States Government as represented by the
// Administrator of The National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
// All Other Rights Reserved.
//
// Author: Wendy C. Shoan
// Created: 2014.04.28
//
/**
Base class definition for the PowerSystem.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#ifndef PowerSystem_hpp
#define PowerSystem_hpp
#include "Hardware.hpp"
#include "gmatdefs.hpp"
#include "SpacePoint.hpp"
#include "SolarSystem.hpp"
// Declare forward reference since Spacecraft owns PowerSystem
class Spacecraft;
/**
Basic power system model attached to Spacecraft.
*/
class GMAT_API PowerSystem : public Hardware
{
public:
PowerSystem(const std::string &systemType, const std::string &nomme);
virtual ~PowerSystem();
PowerSystem(const PowerSystem& copy);
PowerSystem& operator=(const PowerSystem& copy);
/// Initialize the PowerSystem
virtual bool Initialize();
virtual void Copy(const GmatBase*);
/// Set reference objects
virtual void SetSolarSystem(SolarSystem *ss);
virtual void SetSpacecraft(Spacecraft *sc);
virtual bool TakeAction(const std::string &action,
const std::string &actionData = "");
/// Return computed quantities
virtual Real GetBasePower() const;
virtual Real GetPowerGenerated() const = 0; // Total Power Available
virtual Real GetSpacecraftBusPower() const; // Required Bus Power
virtual Real GetThrustPower() const; // Thrust Power Available
virtual void SetEpoch(const std::string &ep);
virtual std::string GetEpochString();
// Parameter access methods - overridden from GmatBase
virtual std::string GetParameterText(const Integer id) const;
virtual std::string GetParameterUnit(const Integer id) const;
virtual Integer GetParameterID(const std::string &str) const;
virtual Gmat::ParameterType
GetParameterType(const Integer id) const;
virtual std::string GetParameterTypeString(const Integer id) const;
virtual bool IsParameterReadOnly(const Integer id) const;
virtual bool IsParameterCommandModeSettable(const Integer id) const;
virtual Real GetRealParameter(const Integer id) const;
virtual Real SetRealParameter(const Integer id,
const Real value);
virtual Real GetRealParameter(const std::string &label) const;
virtual Real SetRealParameter(const std::string &label,
const Real value);
virtual std::string GetStringParameter(const Integer id) const;
virtual bool SetStringParameter(const Integer id,
const std::string &value);
virtual std::string GetStringParameter(const std::string &label) const;
virtual bool SetStringParameter(const std::string &label,
const std::string &value);
virtual std::string GetStringParameter(const Integer id,
const Integer index) const;
virtual bool SetStringParameter(const Integer id,
const std::string &value,
const Integer index);
protected:
/// Epoch format
std::string epochFormat;
/// Initial epoch as input/set
std::string initialEpoch;
/// Initial Maximum Power
Real initialMaxPower;
/// Annual Decay Rate
Real annualDecayRate;
/// Margin
Real margin;
/// Bus Coefficents
Real busCoeff1;
Real busCoeff2;
Real busCoeff3;
/// initialEpoch as a real A1Mjd
Real initialEp;
/// Pointer to the SolarSystem
SolarSystem *solarSystem;
/// Pointer to the Sun
CelestialBody *sun;
/// pointer to the owning Spacecraft
Spacecraft *spacecraft;
/// the origin of the Spacecraft
SpacePoint *scOrigin;
/// Radius of the sun
Real sunRadius;
/// Published parameters for all power systems
enum
{
EPOCH_FORMAT = HardwareParamCount,
INITIAL_EPOCH,
INITIAL_MAX_POWER,
ANNUAL_DECAY_RATE,
MARGIN,
BUS_COEFF1,
BUS_COEFF2,
BUS_COEFF3,
TOTAL_POWER_AVAILABLE, // need these to make Parameters?
REQUIRED_BUS_POWER,
THRUST_POWER_AVAILABLE,
PowerSystemParamCount
};
/// Parameter labels
static const std::string
PARAMETER_TEXT[PowerSystemParamCount - HardwareParamCount];
/// Parameter types
static const Gmat::ParameterType
PARAMETER_TYPE[PowerSystemParamCount - HardwareParamCount];
Real EpochToReal(const std::string &ep);
Real GetSunToSCDistance(Real atEpoch) const;
};
#endif // PowerSystem_hpp
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// NuclearPowerSystem
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// GMAT: General Mission Analysis Tool.
//
// Copyright (c) 2002-2014 United States Government as represented by the
// Administrator of The National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
// All Other Rights Reserved.
//
// Author: Wendy C. Shoan
// Created: 2014.04.28
//
/**
* Base class definition for the NuclearPowerSystem.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#ifndef NuclearPowerSystem_hpp
#define NuclearPowerSystem_hpp
#include "PowerSystem.hpp"
/**
* Basic nuclear power system model attached to Spacecraft.
*/
class GMAT_API NuclearPowerSystem : public PowerSystem
{
public:
NuclearPowerSystem(const std::string &nomme);
virtual ~NuclearPowerSystem();
NuclearPowerSystem(const NuclearPowerSystem& copy);
NuclearPowerSystem& operator=(const NuclearPowerSystem& copy);
virtual bool Initialize();
virtual GmatBase* Clone() const;
virtual Real GetPowerGenerated() const; // Total Power
DEFAULT_TO_NO_REFOBJECTS
protected:
/// Published parameters for nuclear power systems
enum
{
NuclearPowerSystemParamCount = PowerSystemParamCount,
};
};
#endif // NuclearPowerSystem_hpp
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// PowerSystem
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// GMAT: General Mission Analysis Tool.
//
// Copyright (c) 2002-2014 United States Government as represented by the
// Administrator of The National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
// All Other Rights Reserved.
//
// Author: Wendy C. Shoan
// Created: 2014.04.28
//
//
/**
* Class implementation for the Power System.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include "PowerSystem.hpp"
#include "StringUtil.hpp" // for GmatStringUtil
#include "Spacecraft.hpp"
#include "HardwareException.hpp"
#include "MessageInterface.hpp"
#include "GmatConstants.hpp"
#include "TimeSystemConverter.hpp"
#include "GmatConstants.hpp"
#include "GregorianDate.hpp"
#include "DateUtil.hpp"
#include <sstream>
//#define DEBUG_POWER_SYSTEM
//#define DEBUG_POWER_SYSTEM_SET
//#define DEBUG_DATE_FORMAT
//---------------------------------
// static data
//---------------------------------
/// Labels used for the power system parameters.
const std::string
PowerSystem::PARAMETER_TEXT[PowerSystemParamCount - HardwareParamCount] =
{
"EpochFormat",
"InitialEpoch",
"InitialMaxPower",
"AnnualDecayRate",
"Margin",
"BusCoeff1",
"BusCoeff2",
"BusCoeff3",
"TotalPowerAvailable", // ?? need these three or add to CalculationUtilities?
"RequiredBusPower",
"ThrustPowerAvailable",
};
/// Types of the parameters used by fuel tanks.
const Gmat::ParameterType
PowerSystem::PARAMETER_TYPE[PowerSystemParamCount - HardwareParamCount] =
{
Gmat::STRING_TYPE, // "EpochFormat",
Gmat::STRING_TYPE, // "InitialEpoch",
Gmat::REAL_TYPE, // "InitialMaxPower",
Gmat::REAL_TYPE, // "AnnualDecayRate",
Gmat::REAL_TYPE, // "Margin",
Gmat::REAL_TYPE, // "BusCoeff1",
Gmat::REAL_TYPE, // "BusCoeff2",
Gmat::REAL_TYPE, // "BusCoeff3",
Gmat::REAL_TYPE, // "TotalPowerAvailable",
Gmat::REAL_TYPE, // "RequiredBusPower",
Gmat::REAL_TYPE, // "ThrustPowerAvailable",
};
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// PowerSystem()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Power System constructor.
*
* @param systemType type of power system
* @param nomme name for the power system.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PowerSystem::PowerSystem(const std::string &systemType, const std::string &nomme) :
Hardware (Gmat::POWER_SYSTEM, systemType, nomme),
epochFormat ("UTCGregorian"),
initialEpoch ("01 Jan 2000 11:59:28.000"),
initialMaxPower (1.2),
annualDecayRate (5.0),
margin (5.0),
busCoeff1 (0.3),
busCoeff2 (0.0),
busCoeff3 (0.0),
initialEp (21545.0),
solarSystem (NULL),
sun (NULL),
spacecraft (NULL),
scOrigin (NULL),
sunRadius (GmatSolarSystemDefaults::STAR_EQUATORIAL_RADIUS)
{
objectTypes.push_back(Gmat::POWER_SYSTEM);
objectTypeNames.push_back("PowerSystem");
parameterCount = PowerSystemParamCount;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ~PowerSystem()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Power System destructor.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PowerSystem::~PowerSystem()
{
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// PowerSystem(const PowerSystem& copy)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Copy constructor.
*
* This method is called by the Clone method to replicate power systems.
*
* @param copy Reference to the system that gets replicated.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PowerSystem::PowerSystem(const PowerSystem& copy) :
Hardware (copy),
epochFormat (copy.epochFormat),
initialEpoch (copy.initialEpoch),
initialMaxPower (copy.initialMaxPower),
annualDecayRate (copy.annualDecayRate),
margin (copy.margin),
busCoeff1 (copy.busCoeff1),
busCoeff2 (copy.busCoeff2),
busCoeff3 (copy.busCoeff3),
initialEp (copy.initialEp),
solarSystem (NULL),
sun (NULL),
spacecraft (NULL),
scOrigin (NULL),
sunRadius (copy.sunRadius)
{
parameterCount = copy.parameterCount;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// PowerSystem& operator=(const PowerSystem& copy)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Assignment operator.
*
* Sets the parameters for one power system equal to another's.
*
* @param copy Reference to the system that gets replicated.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PowerSystem& PowerSystem::operator=(const PowerSystem& copy)
{
#ifdef DEBUG_POWER_SYSTEM_SET
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("Calling assignment operator on %s\n",
instanceName.c_str());
#endif
if (© != this)
{
Hardware::operator=(copy);
initialMaxPower = copy.initialMaxPower;
epochFormat = copy.epochFormat;
initialEpoch = copy.initialEpoch;
annualDecayRate = copy.annualDecayRate;
margin = copy.margin;
busCoeff1 = copy.busCoeff1;
busCoeff2 = copy.busCoeff2;
busCoeff3 = copy.busCoeff3;
initialEp = copy.initialEp;
solarSystem = NULL;
sun = NULL;
spacecraft = NULL;
scOrigin = NULL;
sunRadius = copy.sunRadius;
}
return *this;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// bool Initialize()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Initializes the Power System.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool PowerSystem::Initialize()
{
isInitialized = true;
return isInitialized;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// void Copy(GmatBase* orig)
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Sets this object to match another one.
*
* @param orig The original that is being copied.
*
* @return A GmatBase pointer to the cloned power system.
*/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void PowerSystem::Copy(const GmatBase* orig)
{
operator=(*((PowerSystem *)(orig)));
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// void SetSolarSystem(SolarSystem *ss)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void PowerSystem::SetSolarSystem(SolarSystem *ss)
{
solarSystem = ss;
sun = solarSystem->GetBody(GmatSolarSystemDefaults::SUN_NAME);
sunRadius = sun->GetEquatorialRadius();
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// void SetSpacecraft(Spacecraft *sc)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void PowerSystem::SetSpacecraft(Spacecraft *sc)
{
if (!sc)
{
std::string errmsg = "Cannot set spacecraft on Power System ";
errmsg += instanceName + ": sc is NULL\n";
throw HardwareException(errmsg);
}
spacecraft = sc;
scOrigin = sc->GetOrigin();
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// bool TakeAction(const std::string &action,
// const std::string &actionData = "")
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool PowerSystem::TakeAction(const std::string &action,
const std::string &actionData)
{
return true; // default action is to do nothing
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Real GetBasePower()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Real PowerSystem::GetBasePower() const
{
Real atEpoch = spacecraft->GetEpoch();
Real yearsFromStart = (atEpoch - initialEp) / GmatTimeConstants::DAYS_PER_YEAR;
#ifdef DEBUG_POWER_SYSTEM
MessageInterface::ShowMessage(
"In PowerSystem::GetBasePower, atEpoch = %12.10f, initialEp = %12.10f\n",
atEpoch, initialEp);
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("yearsFromStart = %12.10f\n", yearsFromStart);
#endif
// Englander Eq. 18
Real basePower = initialMaxPower *
GmatMathUtil::Pow((1 - annualDecayRate/100.00),yearsFromStart);
return basePower;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Real GetSpacecraftBusPower()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Real PowerSystem::GetSpacecraftBusPower() const
{
Real atEpoch = spacecraft->GetEpoch();
Real *state = (spacecraft->GetState()).GetState();
Real sunDist = GetSunToSCDistance(atEpoch);
// Englander: Eq. 19
Real busPower = busCoeff1 + (busCoeff2/sunDist) +
(busCoeff3/(sunDist*sunDist));
#ifdef DEBUG_POWER_SYSTEM
MessageInterface::ShowMessage(
"In PowerSystem::GetSCBasePower, busPower = %12.10f\n",
busPower);
#endif
return busPower;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Real GetThrustPower()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Real PowerSystem::GetThrustPower() const
{
Real atEpoch = spacecraft->GetEpoch();
Real powerGenerated = GetPowerGenerated();
Real busPower = GetSpacecraftBusPower();
// Englander: Eq. 16
Real powerAvailable = (1-margin /100.00) * (powerGenerated - busPower);
if (powerAvailable < 0)
powerAvailable = 0;
#ifdef DEBUG_POWER_SYSTEM
MessageInterface::ShowMessage(
"In PowerSystem::GetThrustPower, powerAvailable = %12.10f\n",
powerAvailable);
#endif
return powerAvailable;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// void SetEpoch(std::string ep)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Set the epoch.
*
* @param <ep> The new epoch.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void PowerSystem::SetEpoch(const std::string &ep)
{
#ifdef DEBUG_DATE_FORMAT
MessageInterface::ShowMessage
("PowerSystem::SetEpoch() Setting epoch for spacecraft %s to %s\n",
instanceName.c_str(), ep.c_str());
#endif
std::string timeSystem;
std::string timeFormat;
TimeConverterUtil::GetTimeSystemAndFormat(epochFormat, timeSystem, timeFormat);
if (timeFormat == "ModJulian") // numeric - save and output without quotes
initialEpoch = GmatStringUtil::RemoveEnclosingString(ep, "'");
else // "Gregorian" - not numeric - save and output with quotes
{
if (!GmatStringUtil::IsEnclosedWith(ep, "'"))
initialEpoch = GmatStringUtil::AddEnclosingString(ep, "'");
else
initialEpoch = ep;
}
#ifdef DEBUG_DATE_FORMAT
MessageInterface::ShowMessage
("PowerSystem::SetEpoch() Calling EpochToReal with %s\n",
initialEpoch.c_str());
#endif
initialEp = EpochToReal(initialEpoch);
#ifdef DEBUG_DATE_FORMAT
MessageInterface::ShowMessage
("PowerSystem::SetEpoch() Setting initialEp (A1Mjd) to %12.15f\n",
initialEp);
#endif
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// std::string GetEpochString()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
std::string PowerSystem::GetEpochString()
{
Real outMjd = -999.999;
std::string outStr;
TimeConverterUtil::Convert("A1ModJulian", initialEp, "",
epochFormat, outMjd, outStr);
return outStr;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// std::string GetParameterText(const Integer id) const
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* This method returns the parameter text, given the input parameter ID.
*
* @param <id> Id for the requested parameter text.
*
* @return parameter text for the requested parameter.
*
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
std::string PowerSystem::GetParameterText(const Integer id) const
{
if (id >= HardwareParamCount && id < PowerSystemParamCount)
return PARAMETER_TEXT[id - HardwareParamCount];
return Hardware::GetParameterText(id);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// std::string GetParameterUnit(const Integer id) const
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* @see GmatBase
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
std::string PowerSystem::GetParameterUnit(const Integer id) const
{
switch (id)
{
case INITIAL_MAX_POWER:
return "kW";
case ANNUAL_DECAY_RATE:
return "percent/year";
case MARGIN:
return "percent";
case BUS_COEFF1:
return "kW";
case BUS_COEFF2:
return "kW*AU";
case BUS_COEFF3:
return "kW*AU^2";
default:
return Hardware::GetParameterUnit(id);
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Integer GetParameterID(const std::string &str) const
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* This method returns the parameter ID, given the input parameter string.
*
* @param <str> string for the requested parameter.
*
* @return ID for the requested parameter.
*
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Integer PowerSystem::GetParameterID(const std::string &str) const
{
for (Integer i = HardwareParamCount; i < PowerSystemParamCount; i++)
{
if (str == PARAMETER_TEXT[i - HardwareParamCount])
return i;
}
return Hardware::GetParameterID(str);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Gmat::ParameterType GetParameterType(const Integer id) const
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* This method returns the parameter type, given the input parameter ID.
*
* @param <id> ID for the requested parameter.
*
* @return parameter type of the requested parameter.
*
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Gmat::ParameterType PowerSystem::GetParameterType(const Integer id) const
{
if (id >= HardwareParamCount && id < PowerSystemParamCount)
return PARAMETER_TYPE[id - HardwareParamCount];
return Hardware::GetParameterType(id);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// std::string GetParameterTypeString(const Integer id) const
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Retrieve the string associated with a parameter.
*
* @param <id> The integer ID for the parameter.
*
* @return Text description for the type of the parameter, or the empty
* string ("").
*/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
std::string PowerSystem::GetParameterTypeString(const Integer id) const
{
return GmatBase::PARAM_TYPE_STRING[GetParameterType(id)];
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// bool IsParameterReadOnly(const Integer id) const
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Checks to see if the requested parameter is read only.
*
* @param <id> Description for the parameter.
*
* @return true if the parameter is read only, false (the default) if not,
* throws if the parameter is out of the valid range of values.
*/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool PowerSystem::IsParameterReadOnly(const Integer id) const
{
if ((id == DIRECTION_X) || (id == DIRECTION_Y) || (id == DIRECTION_Z))
return true;
// These are output only, computed quantities for use as parameters
if ((id == TOTAL_POWER_AVAILABLE) || (id == REQUIRED_BUS_POWER) ||
(id == THRUST_POWER_AVAILABLE))
return true;
return Hardware::IsParameterReadOnly(id);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// bool IsParameterCommandModeSettable(const Integer id) const
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Tests to see if an object property can be set in Command mode
*
* @param id The ID of the object property
*
* @return true if the property can be set in command mode, false if not.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool PowerSystem::IsParameterCommandModeSettable(const Integer id) const
{
// These are output only, computed quantities for use as parameters
if ((id == TOTAL_POWER_AVAILABLE) || (id == REQUIRED_BUS_POWER) ||
(id == THRUST_POWER_AVAILABLE))
return false;
return true; // all settable for now
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Real GetRealParameter(const Integer id) const
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Retrieve the value for a Real parameter.
*
* @param <id> The integer ID for the parameter.
*
* @return The parameter's value.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Real PowerSystem::GetRealParameter(const Integer id) const
{
switch (id)
{
case INITIAL_MAX_POWER:
return initialMaxPower;
case ANNUAL_DECAY_RATE:
return annualDecayRate;
case MARGIN:
return margin;
case BUS_COEFF1:
return busCoeff1;
case BUS_COEFF2:
return busCoeff2;
case BUS_COEFF3:
return busCoeff3;
case TOTAL_POWER_AVAILABLE:
return GetPowerGenerated();
case REQUIRED_BUS_POWER:
return GetSpacecraftBusPower();
case THRUST_POWER_AVAILABLE:
return GetThrustPower();
default:
break; // Default just drops through
}
return Hardware::GetRealParameter(id);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Real SetRealParameter(const Integer id, const Real value)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Set the value for a Real parameter.
*
* This code checks the validity of selected power system parameters.
*
* @param id The integer ID for the parameter.
* @param value The new parameter value.
*
* @return the parameter value at the end of this call, or throw an exception
* if the parameter id is invalid or the parameter type is not Real.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Real PowerSystem::SetRealParameter(const Integer id, const Real value)
{
#ifdef DEBUG_POWER_SYSTEM_SET
MessageInterface::ShowMessage
("PowerSystem::SetRealParameter(), id=%d, value=%f\n", id, value);
#endif
switch (id)
{
case INITIAL_MAX_POWER:
{
#ifdef DEBUG_POWER_SYSTEM_SET
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("Updating initial max power to %lf\n",
value);
#endif
if (value >= 0.0)
{
initialMaxPower = value;
return initialMaxPower;
}
else
{
HardwareException hwe("");
hwe.SetDetails(errorMessageFormat.c_str(),
GmatStringUtil::ToString(value, 16).c_str(),
"InitalMaxPower", "Real Number >= 0.0");
throw hwe;
}
}
case ANNUAL_DECAY_RATE:
if ((value >= 0.0) && (value <= 100.0))
annualDecayRate = value;
else
{
HardwareException hwe("");
hwe.SetDetails(errorMessageFormat.c_str(),
GmatStringUtil::ToString(value, 16).c_str(),
"AnnuaDecayRate", "0 <= Real Number <= 100");
throw hwe;
}
return annualDecayRate;
case MARGIN:
if ((value >= 0.0) && (value <= 100.0))
margin = value;
else
{
HardwareException hwe("");
hwe.SetDetails(errorMessageFormat.c_str(),
GmatStringUtil::ToString(value, 16).c_str(),
"Margin", "0 <= Real Number <= 100");
throw hwe;
}
return margin;
case BUS_COEFF1:
busCoeff1 = value;
return busCoeff1;
case BUS_COEFF2:
busCoeff2 = value;
return busCoeff2;
case BUS_COEFF3:
busCoeff3 = value;
return busCoeff3;
default:
break; // Default just drops through
}
return Hardware::SetRealParameter(id, value);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Real GetRealParameter(const std::string &label) const
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Real PowerSystem::GetRealParameter(const std::string &label) const
{
return GetRealParameter(GetParameterID(label));
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Real SetRealParameter(const std::string &label, const Real value)
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Real PowerSystem::SetRealParameter(const std::string &label, const Real value)
{
return SetRealParameter(GetParameterID(label), value);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// std::string GetStringParameter(const Integer id) const
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
std::string PowerSystem::GetStringParameter(const Integer id) const
{
if (id == EPOCH_FORMAT)
return epochFormat;
if (id == INITIAL_EPOCH)
return initialEpoch;
return Hardware::GetStringParameter(id);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// bool SetStringParameter(const Integer id, const std::string &value)
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool PowerSystem::SetStringParameter(const Integer id, const std::string &value)
{
#ifdef DEBUG_POWER_SYSTEM_SET
MessageInterface::ShowMessage
("PowerSystem::SetStringParameter() entered, id=%d, value='%s'\n", id,
value.c_str());
#endif
if (id == EPOCH_FORMAT)
{
if (TimeConverterUtil::IsValidTimeSystem(value))
{
epochFormat = value;
return true;
}
else
{
HardwareException hwe("");
hwe.SetDetails(errorMessageFormat.c_str(),
value.c_str(),
"EpochFormat", "Valid Time Format");
throw hwe;
}
}
if (id == INITIAL_EPOCH)
{
SetEpoch(value);
return true;
}
return Hardware::SetStringParameter(id, value);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// std::string GetStringParameter(const std::string &label) const
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
std::string PowerSystem::GetStringParameter(const std::string &label) const
{
return GetStringParameter(GetParameterID(label));
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// bool SetStringParameter(const std::string &label, const std::string &value)
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool PowerSystem::SetStringParameter(const std::string &label,
const std::string &value)
{
return SetStringParameter(GetParameterID(label), value);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// std::string GetStringParameter(const Integer id,const Integer index) const
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
std::string PowerSystem::GetStringParameter(const Integer id,
const Integer index) const
{
return Hardware::GetStringParameter(id, index);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// bool SetStringParameter(const Integer id, const std::string &value,
// const Integer index)
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool PowerSystem::SetStringParameter(const Integer id,
const std::string &value,
const Integer index)
{
return Hardware::SetStringParameter(id, value, index);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Protected methods
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Real EpochToReal(const std::string &ep)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Real PowerSystem::EpochToReal(const std::string &ep)
{
Real fromMjd = -999.999;
Real outMjd = -999.999;
std::string outStr;
// remove enclosing quotes for the validation and conversion
std::string epNoQuote = GmatStringUtil::RemoveEnclosingString(ep, "'");
#ifdef DEBUG_DATE_FORMAT
MessageInterface::ShowMessage
("PowerSystem::EpochToReal() Converting from %s to A1ModJulian\n", epochFormat.c_str());
#endif
if (epochFormat.find("Gregorian") != std::string::npos)
{
if (!GregorianDate::IsValid(epNoQuote))
{
std::string errmsg = "PowerSystem error: epoch ";
errmsg += ep + " is not a valid Gregorian date.\n";
throw HardwareException(errmsg);
}
}
TimeConverterUtil::Convert(epochFormat, fromMjd, epNoQuote, "A1ModJulian", outMjd,
outStr);
#ifdef DEBUG_DATE_FORMAT
MessageInterface::ShowMessage
("PowerSystem::EpochToReal() Done converting from %s to A1ModJulian\n", epochFormat.c_str());
#endif
if (outMjd == -999.999)
{
#ifdef DEBUG_DATE_FORMAT
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("PowerSystem::EpochToReal() oops! outMjd = -999.999!!\n");
#endif
}
return outMjd;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Real GetSunToSCDistance(Real atEpoch)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Real PowerSystem::GetSunToSCDistance(Real atEpoch) const
{
Real *state = (spacecraft->GetState()).GetState();
Rvector3 origState = scOrigin->GetMJ2000Position(atEpoch);
Rvector3 sunState = sun->GetMJ2000Position(atEpoch);
Rvector3 sunToOrig = origState - sunState;
Rvector3 scToSun(state[0] + sunToOrig[0], state[1] + sunToOrig[1],
state[2] + sunToOrig[2]);
Real sunSCDist = scToSun.GetMagnitude() /
GmatPhysicalConstants::ASTRONOMICAL_UNIT;
#ifdef DEBUG_POWER_SYSTEM
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("In GetSunToSCDistance ...\n");
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("state = %12.10f %12.10f %12.10f\n",
state[0], state[1], state[2]);
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("origState = %12.10f %12.10f %12.10f\n",
origState[0], origState[1], origState[2]);
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("sunState = %12.10f %12.10f %12.10f\n",
sunState[0], sunState[1], sunState[2]);
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("scToSun = %12.10f %12.10f %12.10f\n",
scToSun[0], scToSun[1], scToSun[2]);
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("sunSCDist = %12.10f\n", sunSCDist);
#endif
return sunSCDist;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// NuclearPowerSystem
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// GMAT: General Mission Analysis Tool.
//
// Copyright (c) 2002-2014 United States Government as represented by the
// Administrator of The National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
// All Other Rights Reserved.
//
// Author: Wendy C. Shoan
// Created: 2014.04.28
//
//
/**
* Class implementation for the Nuclear Power System.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include "NuclearPowerSystem.hpp"
#include "StringUtil.hpp"
#include "HardwareException.hpp"
#include "MessageInterface.hpp"
#include "Spacecraft.hpp"
//#define DEBUG_NUCLEAR
//---------------------------------
// static data
//---------------------------------
// none at this time
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// NuclearPowerSystem()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Nuclear Power System constructor.
*
* @param nomme Name for the power system.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NuclearPowerSystem::NuclearPowerSystem(const std::string &nomme) :
PowerSystem ("NuclearPowerSystem",nomme)
{
objectTypes.push_back(Gmat::NUCLEAR_POWER_SYSTEM);
objectTypeNames.push_back("NuclearPowerSystem");
parameterCount = NuclearPowerSystemParamCount;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ~NuclearPowerSystem()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Nuclear Power System destructor.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NuclearPowerSystem::~NuclearPowerSystem()
{
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// NuclearPowerSystem(const NuclearPowerSystem& copy)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Copy constructor.
*
* This method is called by the Clone method to replicate power systems.
*
* @param copy Reference to the system that gets replicated.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NuclearPowerSystem::NuclearPowerSystem(const NuclearPowerSystem& copy) :
PowerSystem (copy)
{
parameterCount = copy.parameterCount;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// NuclearPowerSystem& operator=(const NuclearPowerSystem& copy)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Assignment operator.
*
* Sets the parameters for one power system equal to another's.
*
* @param copy Reference to the system that gets replicated.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NuclearPowerSystem& NuclearPowerSystem::operator=(const NuclearPowerSystem& copy)
{
#ifdef DEBUG_NUCLEAR
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("Calling assignment operator on %s\n",
instanceName.c_str());
#endif
if (© != this)
{
PowerSystem::operator=(copy);
}
return *this;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// bool Initialize()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Initializes the Nuclear Power System.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool NuclearPowerSystem::Initialize()
{
PowerSystem::Initialize();
return isInitialized;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// GmatBase* Clone() const
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Provides a clone of this object by calling the copy constructor.
*
* @return A GmatBase pointer to the cloned thruster.
*/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
GmatBase* NuclearPowerSystem::Clone() const
{
return new NuclearPowerSystem(*this);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Real GetPowerGenerated()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Real NuclearPowerSystem::GetPowerGenerated() const
{
return GetBasePower();
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Protected methods
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// none at this time
GUI Code
Code examples for the following are included here:
ResourceTree.cpp (selected portions)
GuiItemManager.cpp
PowerSystemPanel.hpp
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// void OnAddHardware(wxCommandEvent &event)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Add a generic hardware to hardware folder
*
* The code used here should be generalizable for other plugin elements as well.
*
* @param <event> command event
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void ResourceTree::OnAddHardware(wxCommandEvent &event)
{
bool isPowerSystem = false;
GmatTree::ItemType itsType = GmatTree::HARDWARE;
// Look up the plugin type based on the ID built with menu that selected it
// NOTE: treating PowerSystems as plugins here as well
std::string selected = pluginMap[event.GetId()];
if (selected.find("PowerSystem") != std::string::npos)
{
isPowerSystem = true;
itsType = GmatTree::POWER_SYSTEM;
}
// The rest is like the other tree additions
wxTreeItemId item = GetSelection();
std::string newName = theGuiInterpreter->GetNewName(selected, 1);
GmatBase *obj = CreateObject(selected, newName);
if (obj != NULL)
{
GmatTree::ItemType dummyType;
GmatTree::ResourceIconType iconToUse;
GetItemTypeAndIcon(obj, dummyType, iconToUse);
wxString name = newName.c_str();
AppendItem(item, name, iconToUse, -1,
new GmatTreeItemData(name, itsType));
Expand(item);
SelectItem(GetLastChild(item));
if (isPowerSystem)
theGuiManager->UpdatePowerSystem();
else
theGuiManager->UpdateSensor();
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// void UpdatePowerSystem(bool updateObjectArray = true)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Updates Power System gui components.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void GuiItemManager::UpdatePowerSystem(bool updateObjectArray)
{
#if DBGLVL_GUI_ITEM_UPDATE
MessageInterface::ShowMessage("===> UpdatePowerSystem\n");
#endif
UpdatePowerSystemList();
if (updateObjectArray)
RefreshAllObjectArray();
}
...
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// wxComboBox* GetPowerSystemComboBox(wxWindow *parent, wxWindowID id,
// const wxSize &size)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* @return Antenna combo box pointer
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
wxComboBox* GuiItemManager::GetPowerSystemComboBox(wxWindow *parent, wxWindowID id,
const wxSize &size)
{
wxComboBox *powerSystemComboBox =
new wxComboBox(parent, id, wxT(""), wxDefaultPosition, size,
thePowerSystemList, wxCB_READONLY);
if (theNumPowerSystem == 0)
powerSystemComboBox->Append("No Power Systems Available");
else
powerSystemComboBox->Insert("", 0);
// show first Power System
powerSystemComboBox->SetSelection(0);
//---------------------------------------------
// register for update
//---------------------------------------------
mPowerSystemCBList.push_back(powerSystemComboBox);
return powerSystemComboBox;
}
...
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// void UpdatePowerSystemList()
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Updates configured Power System list.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void GuiItemManager::UpdatePowerSystemList()
{
StringArray powerSystems =
theGuiInterpreter->GetListOfObjects(Gmat::POWER_SYSTEM);
int numPowerSystems = powerSystems.size();
#if DBGLVL_GUI_ITEM_POWER_SYSTEM
MessageInterface::ShowMessage
("GuiItemManager::UpdatePowerSystemList() numPowerSystems=%d\n",
numPowerSystems);
#endif
theNumPowerSystem = 0;
thePowerSystemList.Clear();
for (int i=0; i<numPowerSystems; i++)
{
thePowerSystemList.Add(powerSystems[i].c_str());
#if DBGLVL_GUI_ITEM_POWER_SYSTEM > 1
MessageInterface::ShowMessage
("GuiItemManager::UpdatePowerSystemList() " + powerSystems[i] + "\n");
#endif
}
theNumPowerSystem = thePowerSystemList.GetCount();
#if DBGLVL_GUI_ITEM_POWER_SYSTEM > 1
MessageInterface::ShowMessage
("GuiItemManager::UpdatePowerSystemList() number of registered ComboBoxes = %d\n",
(Integer) mPowerSystemCBList.size());
#endif
//-------------------------------------------------------
// update registered PowerSystem ComboBox
//-------------------------------------------------------
int sel;
wxString selStr;
for (std::vector<wxComboBox*>::iterator pos = mPowerSystemCBList.begin();
pos != mPowerSystemCBList.end(); ++pos)
{
sel = (*pos)->GetSelection();
selStr = (*pos)->GetValue();
if (theNumPowerSystem > 0)
{
(*pos)->Clear();
(*pos)->Append(thePowerSystemList);
// Insert first item as "No Power System Selected"
if (thePowerSystemList[0] != selStr)
{
(*pos)->Insert("No Power System Selected", 0);
(*pos)->SetSelection(0);
}
else
{
(*pos)->SetSelection(sel);
}
}
}
#if DBGLVL_GUI_ITEM_HW > 1
MessageInterface::ShowMessage
("GuiItemManager::UpdatePowerSystemList() exiting\n");
#endif
} // end UpdatePowerSystemList()
//$Id$
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// PowerSystemPanel
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// GMAT: General Mission Analysis Tool
//
//
// Copyright (c) 2002-2014 United States Government as represented by the
// Administrator of The National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
// All Other Rights Reserved.
//
// Author: Wendy Shoan
// Created: 2014.05.07
/**
* This class contains information needed to setup users spacecraft power
* system through GUI
*
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#ifndef PowerSystemPanel_hpp
#define PowerSystemPanel_hpp
#include "gmatwxdefs.hpp"
#include "Spacecraft.hpp"
#include "GmatPanel.hpp"
#include "GuiItemManager.hpp"
#include "GmatAppData.hpp"
class PowerSystemPanel: public wxPanel
{
public:
PowerSystemPanel(GmatPanel *scPanel, wxWindow *parent, Spacecraft *spacecraft);
~PowerSystemPanel();
void SaveData();
void LoadData();
bool IsDataChanged() { return dataChanged; }
bool CanClosePanel() { return canClose; }
private:
bool dataChanged;
bool canClose;
bool powerSystemChanged;
void Create();
// Event Handling
DECLARE_EVENT_TABLE();
void OnComboBoxChange(wxCommandEvent& event);
Spacecraft *theSpacecraft;
GuiItemManager *theGuiManager;
GuiInterpreter *theGuiInterpreter;
GmatPanel *theScPanel;
wxComboBox *powerSystemComboBox;
std::string thePowerSystem;
// IDs for the controls and the menu commands
enum
{
ID_TEXT = 30220,
ID_COMBOBOX
};
};
#endif
Appendix C: Example (Type 2)
This appendix shows a brief example, illustrating the extra steps needed in order to add an ErrorModel class. After these steps are completed, the remaining work would be similar to Type 1 (see Appendix A). Base Code
- We add an entry in the gmatdefs.hpp
Gmat::ObjectType:
// Estimation types MEASUREMENT_MODEL, // May be replaced by TrackingSystem CORE_MEASUREMENT, // For the measurement primitives ERROR_MODEL, // Error model used in a measurement ...
- We modify the two arrays in
GmatBase, adding "ErrorModel" toOBJECT_TYPE_STRINGafter "CoreMeasurement" and adding a value of "false" to theAUTOMATIC_GLOBAL_FLAGSin the corresponding position. - We create the
ErrorModelclass, making sure to derive it fromGmatBase. We create the corresponding
ErrorModelFactory
- Now we need to tell the
ConfigManagerclass about the newErrorModel. We create an AddErrorModel method and a GetErrorModel:
void AddErrorModel(ErrorModel *meas); ... ErrorModel* GetErrorModel(const std::string &name)
Next we modify Moderator.cpp to register the new ErrorModelFactory. We add an errorModelList to Interpreter. Then we edit Interpreter::BuildCreatableObjectMaps, to add a section for this new list:
errorModelList.clear(); StringArray erm = theModerator->GetListOfFactoryItems(Gmat::ERROR_MODEL); copy(erm.begin(), erm.end(), back_inserter(errorModelList)); copy(erm.begin(), erm.end(), back_inserter(allObjectTypeList)); for (UnsignedInt i = 0; i < errorModelList.size(); i++) objectTypeMap.insert(std::make_pair(errorModelList[i], Gmat::ERROR_MODEL));
- In
Interpreter::GetCreatableList, we add a section to the switch statement for this type as well:
case Gmat::ERROR_MODEL: clist = errorModelList; break;
- To ScriptInterpreter::WriteScript, we add:
//---------------------------------------------
// ErrorModel Objects
//---------------------------------------------
objs = theModerator->GetListOfObjects(Gmat::ERROR_MODEL);
#ifdef DEBUG_SCRIPT_WRITING
MessageInterface::ShowMessage(" Found %d ErrorModels\n", objs.size());
#endif
if (objs.size() > 0)
WriteObjects(objs, "ErrorModels", mode);
We do not need to modify
ObjectInitializerat this time.
GUI Code
The steps for adding a panel and incorporating your new Resource into the other GUI code are identical to steps taken for Type 1 (see Appendix A).